Live
- Stokes motivates his team to put in extra effort, says England pacer Potts
- From overcoming setbacks to leading India in U19 Women’s Asia Cup, Niki Prasad's amazing journey
- Constitution debate: PM Modi hails 'Nari Shakti'; makes strong pitch for 'United Bharat’
- Bihar: Inquiry initiated against principal who went to buy veggies during school hours
- TN: DMK postpones executive meet due to heavy rains & Parliament session
- Porous silicon oxide electrodes can fix durability issues in batteries: Researchers
- Jalandhar civic polls: AAP promises launch of 100 e-buses, round the clock water supply
- Economic upliftment of rural women is priority of Tripura govt: CM Saha
- Rajmata Jijabai Trophy: Manipur move to top of the table, T.N register first win
- Italian envoy Baroli hoping to strengthen ties with India through football
Just In
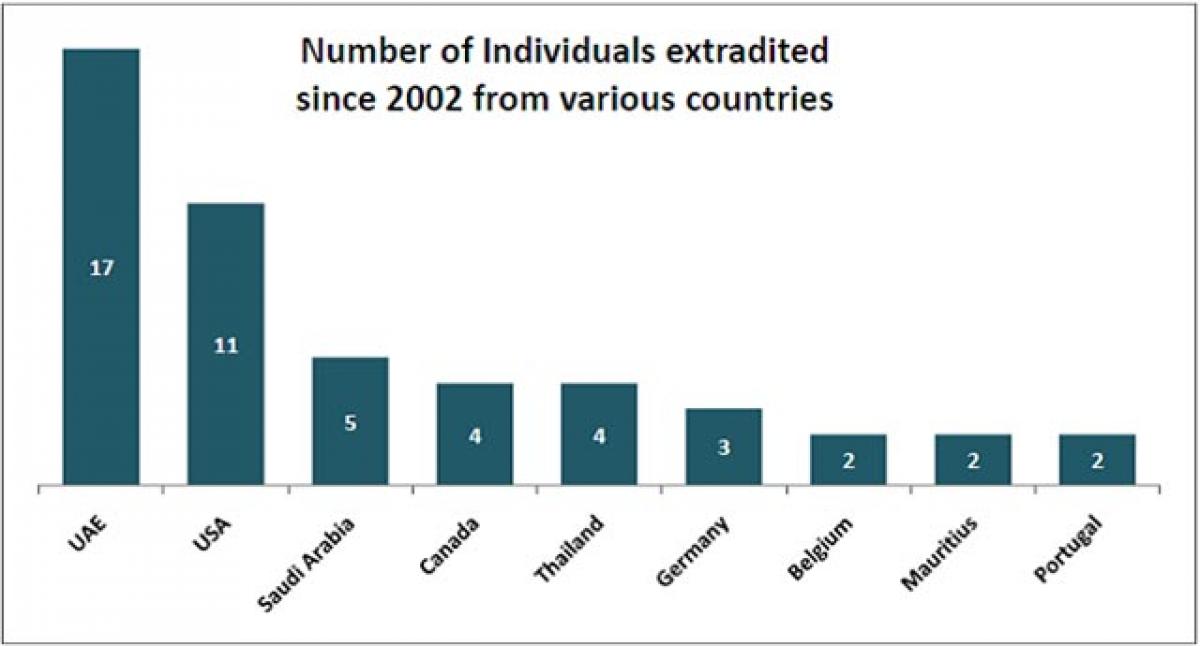
As per data available with the government, 60 individuals were extradited to India since 2002. 17 of them were extradited from UAE followed by 11 from USA. 52 of the extradited were Indian nationals while most of them were extradited for offences like murder and terrorism related charges.
As per data available with the government, 60 individuals were extradited to India since 2002. 17 of them were extradited from UAE followed by 11 from USA. 52 of the extradited were Indian nationals while most of them were extradited for offences like murder and terrorism related charges.
The Government of India (GoI) will reportedly seek extradition of Vijay Mallya after the United Kingdom (UK) rejected the deportation plea. But how easy is it? Though the numbers on the number of extradition/deportation requests made by GoI are not available, government data indicates that only 60 individuals have been deported/extradited to India since 2002.
India has Extradition Treaties with 42 countries. The government also maintains that it is in the process of negotiating extradition treaties with many other countries. India is also a party to various multilateral conventions such as United Nations Convention against Corruption, United Nations Convention against Transnational Organised Crime, International Convention for the Suppression of Terrorist Bombings and the SAARC Regional Convention on Suppression of Terrorism, which can serve as a legal framework to bring back fugitive criminals from the countries who are also the parties to these conventions.
What is the process of extradition?
A request for extradition can be initiated against a fugitive criminal who is formally accused of, charged with or convicted of an extradition offence. Such requests are handled with utmost care so as not to allow the fugitive an opportunity to take measures to avoid getting extradited. The Ministry of External Affairs takes up extradition requests with the foreign countries concerned when a request for extradition is received from the relevant law enforcement agencies in India.
All extradition requests should be supported by documents and information as prescribed by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) guidelines. It has to be noted that each extradition request is different and the request is dependent on the specific treaty/agreement signed with a country. The offence should also be defined in the list of the extradition offences.
The extradition treaty with the UK was signed in the year 1993. This treaty defines the scope of the extradition offence as one which is punishable by law for a term of imprisonment of at least one year. This treaty does not classify political offences as extradition offences. But it provides an exhaustive list of offences that will not be treated as a political offence.
Most individuals extradited from UAE
A total of sixty (60) individuals have been extradited to India from a foreign country since 2002. 19 different countries have extradited people to India. The highest number of extraditions happened from UAE (17) followed by USA (11). Five (5) were extradited from Saudi Arabia while 4 each were extradited from Canada and Thailand. Only one individual Grant Duncan Alexander, a British citizen was extradited from Tanzania and Britain.
Out of the 60 extradited since 2002, 52 of them were Indian nationals, 3 of them were British and one was an American national. Most people were extradited in both 2005 and 2015 when 8 people each were extradited. In both 2003 and 2004, 7 people were extradited. In 2006 and 2009, 5 people were extradited while in 2007 and 2008, 4 each were extradited.
Out of the 60 people extradited since 2002, 13 of them were extradited for murder related charges, 10 each for terrorism related and criminal conspiracy. Eight (8) of them were extradited for economic fraud, while 3 each were extradited for sexual abuse of children and waging war against India. The other offences include attempt to murder, cheating, forgery, drug offences and passport fraud etc. (Courtesy: https://factly.in)
By Rakesh Dubbudu

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







