3D Ultrasonography: Revolutionising Routine Sonography
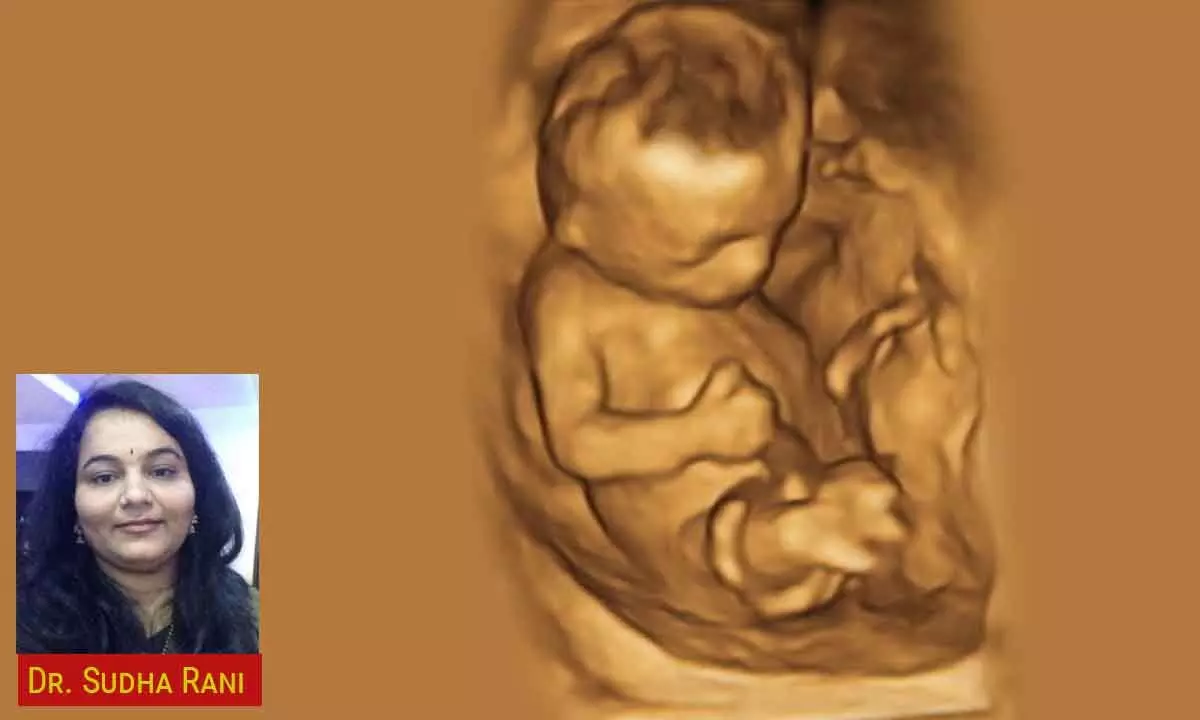
Dr Sudha Rani speaks about how 3D ultrasonography is becoming an integral part of routine sonography
Dr. Sudha Rani, a senior radiologist from India, enthusiastically affirms that 3D ultrasonography is becoming an integral part of routine sonography. She reflects on the past when the potential of 3D USG was unclear, and ultrasonography was losing ground to higher imaging modalities such as CT scans and MRI due to its limited display capabilities. However, with the advent of 3D imaging technology, ultrasound has resurfaced as a formidable competitor of MRI and CT scans in terms of the latest technology, safety and convenience for radiologists.
The introduction of 3D imaging has significantly simplified the job for radiologists by enabling the generation of three-dimensional representations of the target area. Various technological advancements, including surface rendering, automatic volume scan, multiplane volume analysis, and power Doppler qualification, have facilitated this transition and made the process more efficient.
Presently, ultrasound is routinely employed in gynecology and obstetric imaging due to its convenience. For instance, in cases of infertility, assessing the shape of the uterus in three dimensions becomes crucial to identify anomalies that might contribute to pregnancy failures. Traditional 2D ultrasound imaging falls short in accurately evaluating such anomalies.
In the past, MRI was the standard method for evaluation. However, with the advancements in 3D applications, Ultrasonography has become a reliable technique for accurately diagnosing anomalies.
When it comes to assessing uterine cavity lesions and endometrial pathology, Volume ultrasonography has emerged as the modality of choice. Previously, conventional hysterosalpingography under fluoroscopic guidance was used to evaluate endometrial cavity lesions and fallopian tube blockages. However, Sonosalpingogram, has gained popularity for the same purpose . 3D contrast, inversion mode, provides clear visualization of the fallopian tubes.
In cases of infertility, basal ovarian volume and Antral follicular count are assessed. Nowadays, software applications offer customized volume scans and multi-planar volume analysis for this purpose.
Recent advancements in automated ultrasound software techniques have revolutionized volume calculation through 3D VOCAL technology. This technique allows for mean diameter and volume measurements of each follicle, enabling a detailed study of follicles through color-coded representations.Furthermore, 3D power Doppler indices have proven to be more effective in assessing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) compared to 2D power indices.
In evaluating endometrial receptivity, ovary response, and pre-HCG follicular and endometrial evaluation, Volume USG –VOCAL and color histogram techniques provide additional value. Endometrial receptivity plays a crucial role in infertility cases. 3D imaging assists in assessing parameters such as endometrial volume, texture, uterine vascularity, and vascularity of the endometrium and sub endometrium (VI, FI, and VFI in endometrial and sub endometrial zones).
The three-dimensional assessment of perifollicular vascularity offers comprehensive information across all planes, aiding in the identification of mature and fertilizable oocytes.
The applications of 3D ultrasound extend beyond reproductive medicine. Radiologists utilise these techniques to demonstrate fetal anomalies, employing methods like surface rendering for
fetal 2D echo that yield tomographic images and simplify acquisition. Vascular imaging, ophthalmic tumor volume and vascularity evaluation, and assessment of treatment response in head and neck carcinomas through lymph node tracing are also areas benefiting from 3D ultrasound technology.
To further enhance the capabilities of 3D ultrasonography, companies are developing “fly through” applications that provide internal views of tubular structures. This technique finds utility in virtual colonoscopy, virtual ductography, and virtual hysteroscopy. Moreover, blood vessels such as the aorta, portal vein, hepatic veins, carotid vein, and peripheral veins can be assessed using these advancements.
The key advantages of 3D ultrasonography lie in its non-ionizing radiation, making it a safer alternative, as well as its ease of use, affordability, high speed, and accessibility.
However, there are certain limitations to consider. The availability of expertise, time consumption, and computational challenges remain significant hurdles that need to be addressed.
In conclusion, 3D ultrasonography represents a remarkable technological advancement that is rapidly gaining prominence. Its ability to accurately reproduce anatomical views and enable
precise volume measurements has profound implications assisting physicians and surgeons planning the patient management. Widespread awareness, training, and the development of 2D to 3D imaging conversion of machinery are necessary to fully exploit the potential of this technology. Although it may require additional expertise and computational resources, 3D ultrasonography offers lower radiation exposure to patients and affordability.
(Mail id: [email protected] Ph: 040-67669999; 8520004421)














