Acids, bases and water
One of the most interesting parts of chemistry is the study of acids and bases Its also a very practical aspect of chemistry, since we use acids and bases every day For instance, although acidic probably doesnt spring to mind when you bite into a tomato, youre actually tasting acidic juice
One of the most interesting parts of chemistry is the study of acids and bases. It’s also a very practical aspect of chemistry, since we use acids and bases every day! For instance, although ‘acidic’ probably doesn’t spring to mind when you bite into a tomato, you’re actually tasting acidic juice.
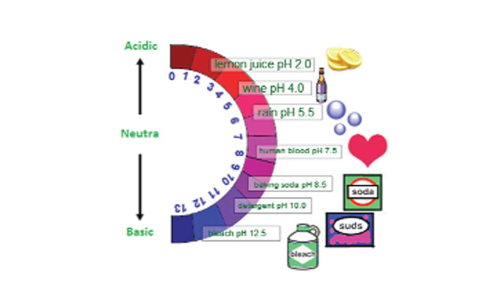
One of the characteristics of acids is that they taste sour. Bases, on the other hand, have a bitter taste. The sour or bitter taste is one of the easy ways to tell whether a food or drink is acidic or basic, although it’s not safe to use the taste test with other things.
When dissolved in water, acids donate hydrogen ions (H+). Hydrogen ions are hydrogen atoms that have lost an electron and now have just a proton, giving them a positive electrical charge. Bases, on the other hand, mixed with water yield hydroxide ions (OH-). If a solution has a high concentration of H+ ions, then it is acidic. If a solution has a high concentration of OH- ions, then it is basic.
In many acid-base reactions, the resulting product is water along and a salt. If hydrochloric acid (HCL) and the base sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are combined, the product is H2O (water) and NaCl (sodium chloride, a table salt). The H+ ions in the acid join with and are neutralized by the OH- ions of the base to form H2O.
One of the simplest activities to show how acids and bases react with each other (and to demonstrate their different properties) is to make a baking soda and vinegar ‘volcano’. To make a big eruption, use a small plastic bottle (the size 20-oz soft drinks come in works well). Fill the bottle halfway (1 to 1.5 cups) with vinegar.
To start the eruption, drop a baking soda ‘bomb’ into the bottle—wrap one tablespoon of baking soda into a small piece of tissue paper, tying the ends with thread. You should see an instant eruption! The baking soda, a base, neutralizes the acid in vinegar. This releases carbon dioxide gas, which causes the fizzing action in your volcano. (An acidic solution is neutralized when a base is added to it, and a basic solution is neutralized by the addition of an acid.)
For another reaction experiment, put an Alka-Seltzer tablet in the bottom of a clear plastic film canister (the kind where the cap fits inside instead of closing over the outside).








