Live
- Fierce battle ahead: Kejriwal faces off against sons of former CMs in New Delhi Assembly seat
- Police Attempt to Seize Mohan Babu’s Gun in TV9 Reporter Attack Case
- A feminist lens on our mythology
- Prakasam police rescues kidnapped toddler within hours
- Time to get rid of Sattavad and Parivarvad politics
- Extend neither spl nor ill treatment
- Must-Watch OTT Originals in 2024: The Year’s Best Shows and Movies
- 40 Indian startups secure over $787 mn in a week
- India now formidable force on chess board
- Raghavendra Mutt pontiff visits Tirumala
Just In
Financial services are being provided by the financial institutions such as banks, insurance companies, pension agencies, micro-finance institutions, stock markets etc.
Financial services are being provided by the financial institutions such as banks, insurance companies, pension agencies, micro-finance institutions, stock markets etc. These institutions mobilize savings and allocate credit to business, thus becoming a sine-qua-non for the development of business. While financial sector includes a range of financial institutions, penetration of financial sector is analysed with the help of information available on commercial banks, which constitutes a significant portion of the financial sector in India.
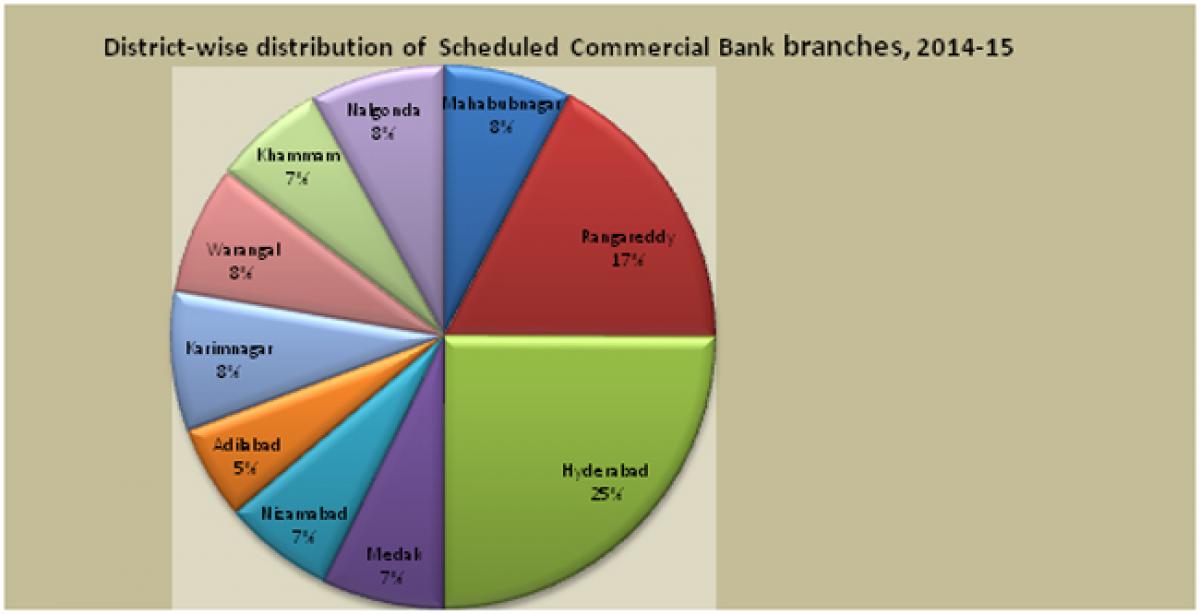
The district-wise concentration of Schedule Commercial Banks reveals that one-fourth of the scheduled commercial banks is in the Hyderabad district (see Figure 5.6). Hyderabad & Rangareddy districts together account for around 42 percent of the total scheduled commercial bank branches in the State. Adilabad is having the lowest number of bank branches per thousand population in the State.
Table: District-wise Banking Indicators in Telangana during 2014-15
| Sl No | Districts | All Scheduled Bank | Population per (000’s) | Credit (Rs. in crore) | Deposit (Rs. in crore) | credit-deposit ratio |
| 1 | Mahabubnagar | 337 | 12 | 6,841 | 5,688 | 120 |
| 2 | Rangareddy | 762 | 7 | 21,290 | 46,908 | 45 |
| 3 | Hyderabad | 1,094 | 4 | 2,35,448 | 1,91,709 | 123 |
| 4 | Medak | 315 | 10 | 9,087 | 8,032 | 113 |
| 5 | Nizamabad | 289 | 9 | 6,266 | 5,669 | 111 |
| 6 | Adilabad | 243 | 11 | 5,317 | 6,105 | 87 |
| 7 | Karimnagar | 365 | 10 | 7,577 | 10,610 | 71 |
| 8 | Warangal | 337 | 10 | 8,742 | 9,303 | 94 |
| 9 | Khammam | 291 | 10 | 6,864 | 7,165 | 96 |
| 10 | Nalgonda | 350 | 10 | 8,322 | 5,648 | 147 |
| Total | 4,383 | 8 | 3,15,754 | 2,96,836 | 106 |
Source: Reserve Bank of India
Indicators, such as population per bank and Credit-Deposit Ratio (CDR), are used for showing the extent of banking penetration. On an average, each bank branch is serving around 8000 population in 2014 as against 14000 per bank branch at all-India level. Credit-Deposit Ratio (CDR) in the State is about 106. Inter-district analysis reveals that Rangareddy, Karimnagar, Adilabad, Warangal and Khammam districts have CDR less than 100 percent.
| Financial Inclusion |
| Growth theories argue that capital is primary not only for growth of the economy but also for poor catch up with the rest of the population. Capital is required for multiple reasons: Short-run capital requirement for buying raw material, fertilizer, pesticides, seeds, repair and maintenance of implements, paying rent etc. (ii) long-run capital requirement include expenditure on education, health, investment for enterprise, construction of house, cattle, implements, digging a well for irrigation purpose, procurement of land etc. (iii) Consumption needs especially during lean periods, drought, flood, or crop failure and (iv) for unproductive purposes such as social and religious functions, festivals, litigation etc. Access to finance by the poor and vulnerable groups is a prerequisite for poverty reduction and social cohesion. Financial inclusion denotes delivery of financial services at an affordable cost to vast sections of the disadvantaged and low-income groups. Traditionally financial inclusion is understood as opening new bank branches and bank accounts in rural and unbanked areas. But now financial inclusion is seen to be something more than mere opening bank branches. Financial inclusion means easy access to various financial services such as credit, savings, insurance and payments and remittance facilities by every citizen irrespective of his/her economic status. Both State and Central Government has initiated number of programs for financial inclusion such as encouraging SHG-Banking linkage programs, Jan Dhan Yojana, etc. |
Outlook for the Services Sector
The services sector has been the main source of growth of the State economy. Availability of good quality infrastructure, educated and highly skilled professionals, with a cost advantage has helped the state to maintain double-digit growth in the sector. At present, only 23 percent of the total workforce (rural and urban) in the state is employed in the service sector and it contributes about 61 percent to State’s GVA. Hence, there is scope for increase in the employment share of this sector. Within the Services sector, more focus needs to be given to Information, Communication, and Technology (ICT), tourism, financial sector for employment generation.
A government has been using ICT for effective delivery of services for common people. A number of e-Governance initiatives have been taken up by the Government, which resulted in a positive impact on the peoples' lives.
The government started ‘Digital Telangana’ programme to facilitate digital empowerment of all its citizens. Tourism is one of the sectors, which has huge potential for income and employment generation in the State. After formation of the State, concerted efforts are being made to build a brand for 'Telangana Tourism'.
The biggest challenge that the State is facing in Services sector is, the skill gap that exists in students who just passed out of colleges and universities and industry requirements. In order to fill the skill deficit, the Government has established Telangana Academy for Skill & Knowledge (TASK) to bring industry and academia on a single platform. This initiative is expected to increase the employability of students by imparting skills needed for the industry.
G.Rajendera Kumar

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







