“A woman’s health is her capital “: Fibroids?
Do all fibroids require to be removed
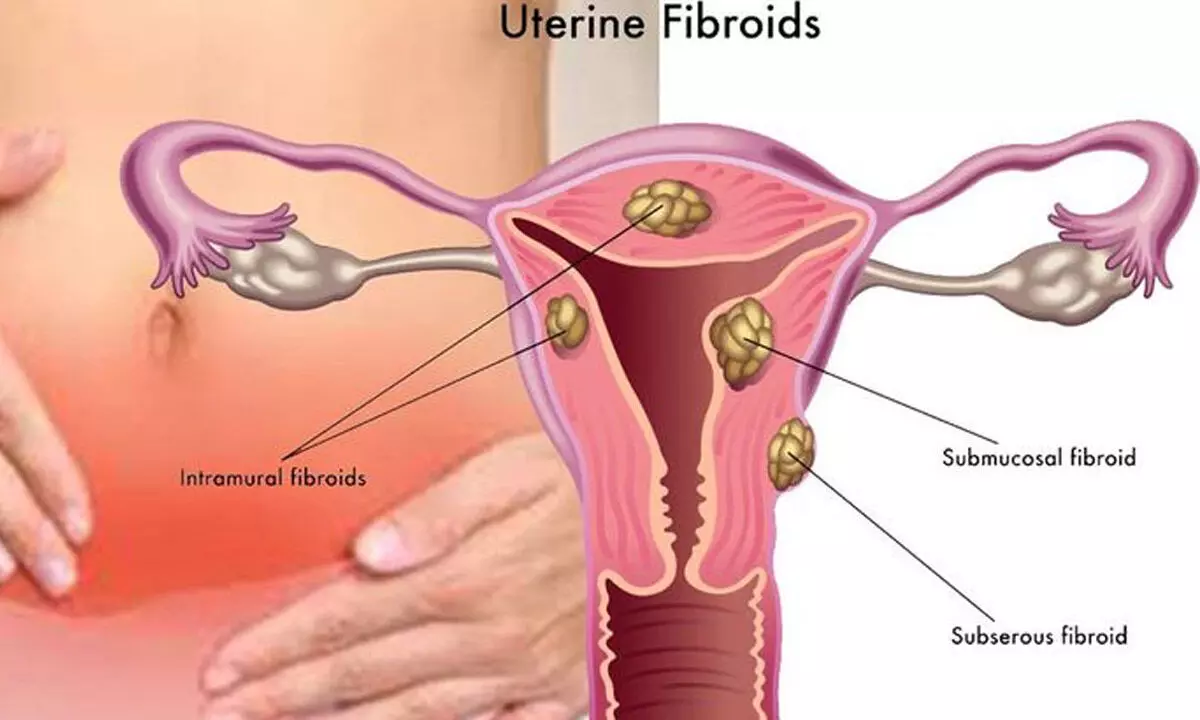
Dr Sri Harika Bonam are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the womb (uterus). They are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and are also known as uterine myomas or leiomyoma’s. 60-70% women develop fibroids in their lifetime or by the age of 50. Half of them do not have any symptoms. Uterine Fibroid is also the leading cause of hysterectomy in our country.
Size of the fibroid can vary from few mms to up to 20-30 cm. They can be located in the lining of womb, within the wall, in the outer layer of the womb or in the broad ligament. Depending on the size, location, rapidity of the growth they can present with wide variety of symptoms.
They include: -
l heavy bleeding during periods
l tummy (abdominal) pain during periods or in between periods
l lower back pain
l Frequent urination
l Difficulty in passing stools.
l pain or discomfort during sex.
l Irregular inter menstrual bleeding
In rare cases, it can cause difficulty in conceiving.
Why do fibroids develop?
The exact cause is unknown, but they have been linked to the hormone oestrogen, the female reproductive hormone produced by the ovaries.
Oestrogen levels are at their highest in the reproductive age of 16 to 50years, so are the fibroids.
They tend to shrink when oestrogen levels are low, such as after menopause. It’s also thought they occur more often in overweight/ obese because being overweight increases the level of oestrogen in the body.
Fibroids are thought to develop more frequently in women of African-Caribbean origin. Studies also suggest that there is a possible genetic cause.
Who needs treatment?
Treatment may not be necessary if you do not have any symptoms, or if you only have minor symptoms that are not significantly affecting your everyday activities.
Fibroids often shrink after menopause and symptoms will disappear gradually.
What are the treatment options for fibroids?
Treatment depends on the age; type and severity of symptoms; location, number and size of fibroids; fertility concerns; response to any previous treatments & patient’s wishes.
1st line is medical; which could be no hormonal or hormonal, that reduce the bleeding/ shrink the fibroids. Failing which, further options would be non-surgical and surgical options.
Non-surgical options include MIRENA, Uterine artery embolization, MRI guided procedures.
MIRENA - a small ‘T’ shaped plastic device that releases progesterone hormone slowly inside the womb which gradually shrinks the fibroid size and gives symptomatic relief. MIRENA also has a benefit of acting as a contraceptive method. Side effects include irregular bleeding, spotting & up to 1/3rd may not respond and may end up requiring surgery.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is an alternative to surgery & may be recommended for women with large fibroids. It a procedure done under local anaesthesia, in which blood vessels that supply the fibroids are blocked with gel/ foam like particles causing them to shrink. Side effects include excess vaginal discharge, pain … can last up to few days to weeks post procedure and up to 1/5th may not have symptomatic relief, necessitating surgery on a later date.
MRI guided procedures like focused ultrasound or percutaneous laser ablation are relatively new techniques for treating fibroids, and the long-term benefits and risks are unknown.
What are the surgical options?
Surgery may be considered if symptoms are severe and have not responded to medical management. The two main types of surgery done for fibroids are: -
l myomectomy - procedure to remove the fibroid and suture the womb,
l hysterectomy - removal of womb.
Which one to be decided, depends on multiple factors like women’s age; number, site and size of fibroids; family completed or not; any associated medical problems and women’s choices after counselling pros and cons of both the procedures.
Either of the procedures can be done by keyhole method(laparoscopy) of surgery which has many advantages over conventional open surgery, like less blood loss, less complications, early recovery, early discharge and better satisfaction.
“I got 99 problems but having a uterus ain’t one”.
Does Fibroids in pregnancy cause any complications?
Women with fibroids in pregnancy may experience tummy (abdominal) pain during pregnancy, and there’s a risk of preterm labour.
If large fibroids block the vagina, a caesarean section might be necessary. Women with fibroids also tend to have excess bleeding after delivery or during caesarean section.
(Dr Sri Harika Bonam, Consultant Obstetrician & Gyneacologist & Lap Surgeon, Apollo Cradle & Children’s Hospital, Hyderabad)














