Live
- Gurumurthy takes charge as chief of Gowda Corpn
- Study warns: Ultra-processed foods may accelerate biological age
- CM pledges more political opportunities to Madigas
- Year-Ender 2024 Guide: Home remedies to relieve Period Pain.
- All India crafts mela begins today
- TTD gears up for Vaikunta Ekadasi fete
- Vizag attracts tourists as much as Kashmir
- Express Yourself
- Rajadhiraaj: Love. Life. Leela
- Students immerse in nature in Chilkur forest
Just In
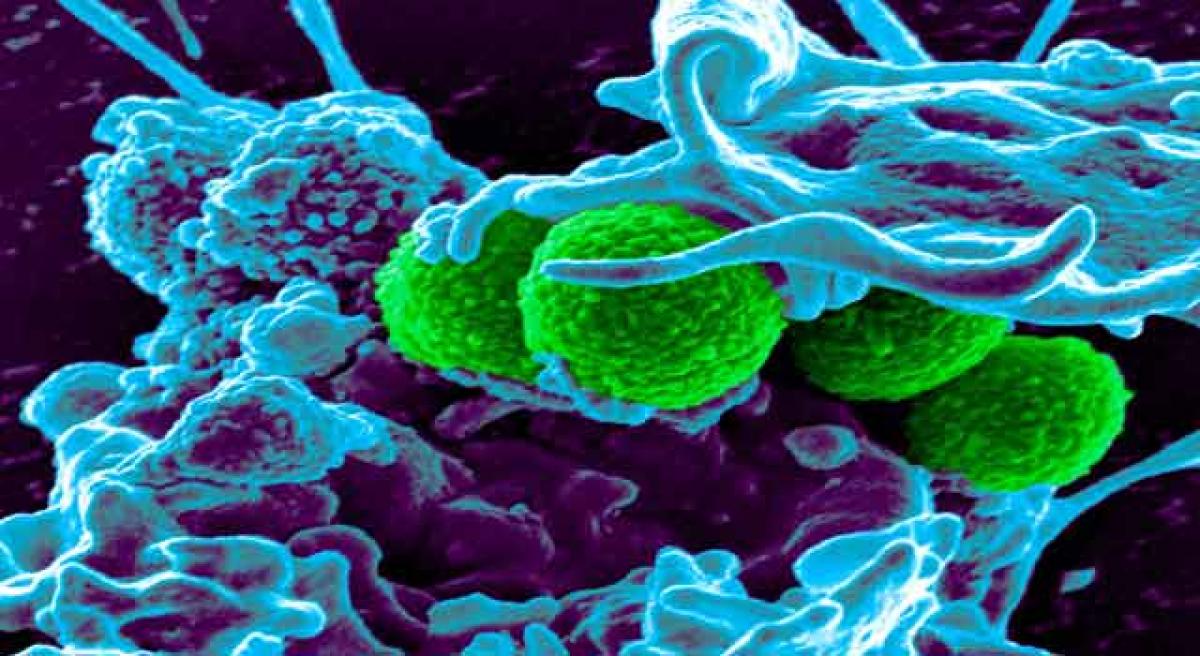
In a major step towards bringing to the clinic a “game-changing” new antibiotic that was discovered last year, a team of University of Lincoln researchers, including one of Indian-origin, has successfully produced two synthetic derivatives of Teixobactin.
London: In a major step towards bringing to the clinic a “game-changing” new antibiotic that was discovered last year, a team of University of Lincoln researchers, including one of Indian-origin, has successfully produced two synthetic derivatives of Teixobactin.
Last year, the discovery of the antibiotic Teixobactin by researchers in the US was hailed as a ‘game-changer’ in the fight against antimicrobial resistance as it is the world’s first known antibiotic capable of destroying “drug resistant” bacteria.
The last new class of antibiotics was discovered nearly 30 years ago. However, in order for Teixobactin to be developed as a potential drug treatment, several versions of the antibiotic must be produced via chemical synthesis in order to overcome the hurdles of drug development.
Researchers in laboratories around the world have been working towards this objective since last year’s breakthrough.
"Teixobactin originally evolved in soil to kill the bacteria around it, so our challenge was to produce the antibiotic synthetically,” said Singh, a specialist in novel drug design at Lincoln’s School of Pharmacy.
"The method we created to do this uses commercially available ‘building blocks’ and has a single purification step, and we are delighted with the results - we are now able to present the total synthesis of two derivatives of Teixobactin,” Singh noted.
The bacteria against which Teixobactin is effective have, thus far, not shown any detectable resistance and given its mechanisms of attack, scientists are also confident that this is unlikely to occur in the future.

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







