Live
- A Soulful Celebration of Global Music
- Brahmin Community delegation felicitates CM Saini
- Allu Arjun Visits Chiranjeevi’s House for Lunch Meet
- Toyota organising TG Grameena Mahotsav
- Special rituals conducted at Maramma Temple
- Siddaramaiah has special love for Muslims: BJP
- We can’t afford spending less than 6% of GDP on healthcare
- Guinness World Record for continuous Hanuman Chalisa chanting
- REMOTE TRIBAL AREA TO GET NEW BRIDGE
- Dr LB College, Woxsen teams win in Climate Tank Accelerator event
Just In
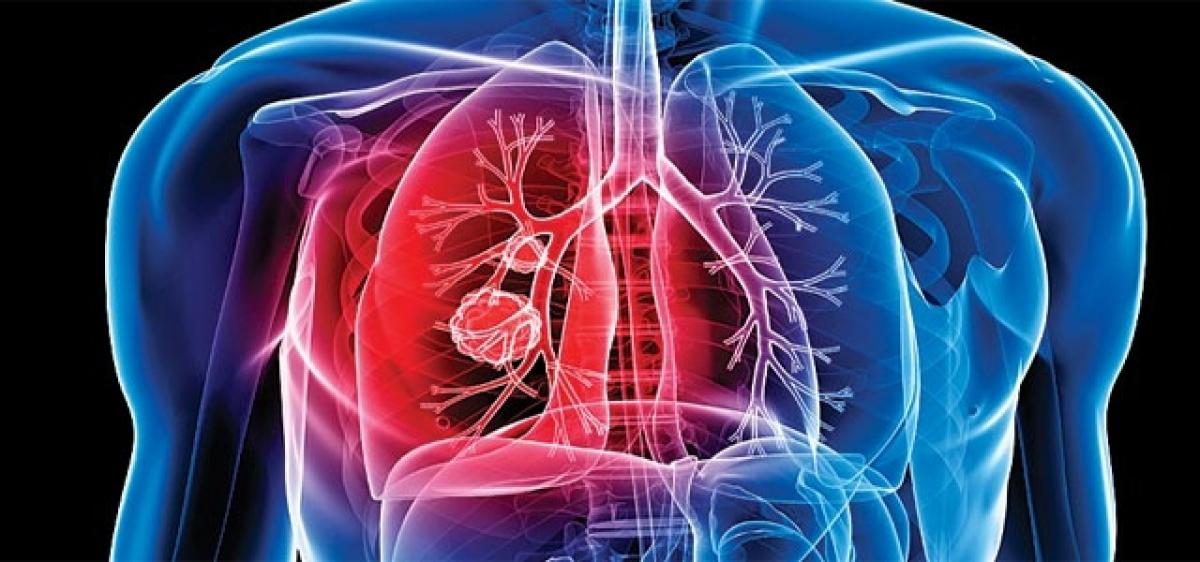
Over 500 cases of Brain TB (TBM-mycobacterium tuberculosis ) were reported in Telangana State in the first 11 months of 2016, according to a shocking claim made by the Helping Hand Foundation (HHF), a city-based NGO that released a report on Thursday after extensive field studies.
Hyderabad: Over 500 cases of Brain TB (TBM-mycobacterium tuberculosis ) were reported in Telangana State in the first 11 months of 2016, according to a shocking claim made by the Helping Hand Foundation (HHF), a city-based NGO that released a report on Thursday after extensive field studies.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), India is reporting 3 million new cases of TB each year (2.84 million in 2015) and bears 30 % of world’s TB burden. Yet, data on TBM is not available with the government as it is still not a notified disease.
HIGHLIGHTS:
- 30% of global TB burden reported in India
- Data on TBM (mycobacterium tuberculosis) is not available with the government as it is not a notified disease
- Patient has to spend between 1 lakh and 3 lakh; Aryogyasri cover limited to 20,000 in State
Brain TB or TBM (mycobacterium tuberculosis) is infection of the meninges —the system of membranes that envelops the central nervous system. Meninges can be infected by viral and fungal strains. Among the three strains, TBM is more virulent and chronic form of infection that affects the meninges.
Tuberculous meningitis is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis. More than 50% of the TBM patients sought treatment in private hospitals. On an average, a patient spends between Rs 1 lakh and Rs 3 lakh. TS Health Aryogyasri scheme covers TBM to the extent of Rs 20,000 only.
Mujtaba Hasan Askari, founder-trustee of HHF, said that TBM per se was not contagious -- perhaps the main reason why all extra pulmonary TB cases have not yet caught the attention of health authorities running the National TB programme.
Dr Afshan Jabeen, Addl Professor of Neurology, NIMS, says, “Undiagnosed and untreated TBM may lead to permanent loss of vision, loss of limb function, seizures and even death. Early diagnosis of the disease is key to long-term survival and reducing the risk of morbidity in patients.”
Another major challenge, according to Dr Jabeen, is cases of TBM today are drug-resistant (MDR TBM). So, newer diagnostic tools like Genexpert TB test & other molecular tests to rule out drug resistance to one or more TB drugs are vital for establishing drug resistance form of TBM so that appropriate treatment options for the disease are started in time.
Presently, the Genexpert test is available in a few private hospitals and in the State-run Chest Hospital -- the nodal centre for TB.
However, only two tests are free. For the third time, the patients are asked to get this done outside in private labs and the cost of the same is between Rs 1100/ and Rs 1800/- for white card holders.
NIMS, however, is running a pilot project on Genexpert free of cost for suspected cases of MDR TB.
Dr B Ranga Reddy, President, Infection Control Academy of India (IFCAI) & Advisor, Public Health Foundation of India, said, “While in India we are talking about MDR, the West is talking about Extremely Drug Resistance (EDR).
Anti Microbial Resistance (AMR) is the biggest health crisis the world is facing today and it will only aggravate if left out.” Presently, all forms of extra pulmonary TB are not part of the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP).
This only adds to the confusion and has contributed to the sordid state of affairs in policy with regard to management of TB.
It is critical for the State TB office to look into some of the policy gaps in TS for reaching out to patients suffering from all forms of TB, according to Askari.

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







