What is Particulate Matter (PM)?
Subtypes of atmospheric particulate matter include suspended particulate matter (SPM), thoracic and respirable particles, inhalable coarse particles, which are [coarse] particles with a diameter between 2.5 and 10 micrometres (μm), fine particles with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less PM2.5 ,PM10 ultrafine particles, and soot The IARC and WHO designate airborne particulates a Group 1 carcinogen.
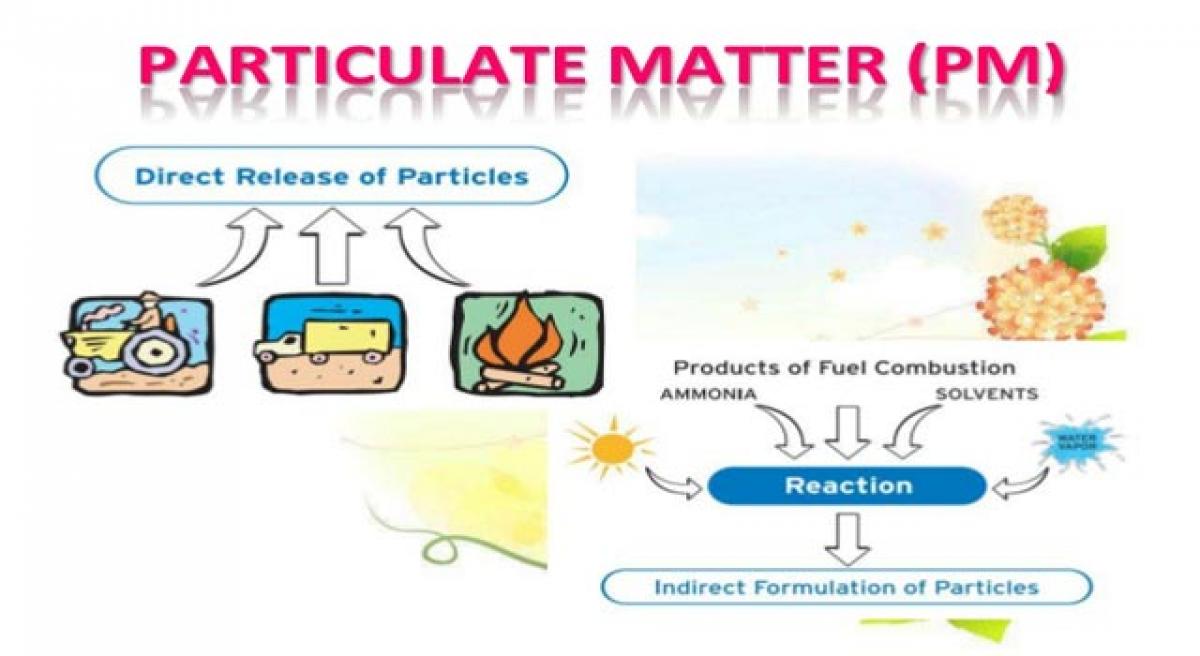
Atmospheric particulate matter – also known as particulate matter (PM) or particulates – are microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in the Earth's atmosphere. The term aerosol commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Sources of particulate matter can be man-made or natural. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health.
Subtypes of atmospheric particulate matter include suspended particulate matter (SPM), thoracic and respirable particles, inhalable coarse particles, which are [coarse] particles with a diameter between 2.5 and 10 micrometres (μm), fine particles with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less PM2.5 ,PM10 ultrafine particles, and soot The IARC and WHO designate airborne particulates a Group 1 carcinogen.
Particulates are the deadliest form of air pollution due to their ability to penetrate deep into the lungs and blood streams unfiltered, causing permanent DNA mutations, heart attacks, and premature death. In 2013, a study involving 312,944 people in nine European countries revealed that there was no safe level of particulates and that for every increase of 10 μg/m3 in PM10, the lung cancer rate rose 22%. The smaller PM2.5 were particularly deadly, with a 36% increase in lung cancer per 10 μg/m3 as it can penetrate deeper into the lungs.
Atmospheric aerosols affect the climate of the earth by changing the amount of incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial long wave radiation retained in the earth's system. This occurs through several distinct mechanisms which are split into direct, indirect and semi-direct aerosol effects. The aerosol climate effects are the biggest source of uncertainty in future climate predictions



















